Episode Footnotes
According to Jerry Pournelle’s Iron Law of Bureaucracy, in any bureaucracy, the people devoted to the benefit of the bureaucracy itself always gain control, and those dedicated to the goals the bureaucracy is supposed to accomplish have less and less influence, and are sometimes eliminated entirely.
According to Edgar Schein, learning anxiety is the feeling that if we allow ourselves to enter a learning or change process or if we admit to ourselves and others that something is wrong or imperfect, we will lose our effectiveness, our self-esteem, and maybe even our identity.
Journey and roadmap are common terms likely used by your stakeholders. We believe the terminology suggested by Erik Hollnagel, terms such as voyage and nautical chart, are more applicable since there is no regularly travelled known road to implementing human and organizational performance. However, in this case, we use the language of stakeholders.
A project charter typically includes the project requirements, the business needs, a summary schedule, assumptions and constraints.
Sidney Dekker describes a Looking Good Index as a negative outcome of bureaucracy where metrics are manipulated to obscure poor performance.
BioPhorum is a global collaboration of biopharmaceutical industry leaders. BioPhorum’s purpose as stated on their website is “To solve pertinent pre-competitive industry challenges, improve operational best practices, and engage with key industry stakeholders.” More information can be found at https://www.biophorum.com/.
A pre-job brief is a conversation among people who will be performing a work activity. This includes a discussion about risks associated with the work, and how risks will be managed. Pre-job briefs are covered in more detail in chapter twelve.
Positive control is when all that happens is as intended, and nothing else happens.
Performance management is an ongoing process of communication between a supervisor and an employee that occurs throughout the year, in support of accomplishing the strategic objectives of the organization. The communication process includes clarifying expectations, setting objectives, identifying goals, providing feedback, and reviewing results.
Sharp-end is a way of saying that the person is ‘in touch’ and appreciates the actualities of the work. It is roughly equivalent to the British and Australian idiom “at the coalface”, which refers to the workplace of an underground mine worker where coal is being cut from the rock, and these workers being directly involved with the core of the business.
Humble Consulting is the title of a book by Edgar Schein in which he describes how consultants can be more effective and helpful by working with clients in a more personal way, with authentic openness, curiosity, and humility.
Gemba is a Japanese word for the actual place, and when used as part of Lean it refers to the place where the actual work is done.
Human beings enjoy the exercise of their realized capacities (their innate or trained abilities), and this enjoyment increases the more the capacity is realized, or the greater its complexity.
The Harm Principle originates from the book, On Liberty, written by John Stuart Mill. The subject passage reads “The only purpose for which power can be rightfully exercised over any member of a civilized community, against his will, is to prevent harm to others. His own good, either physical or moral, is not sufficient warrant.”
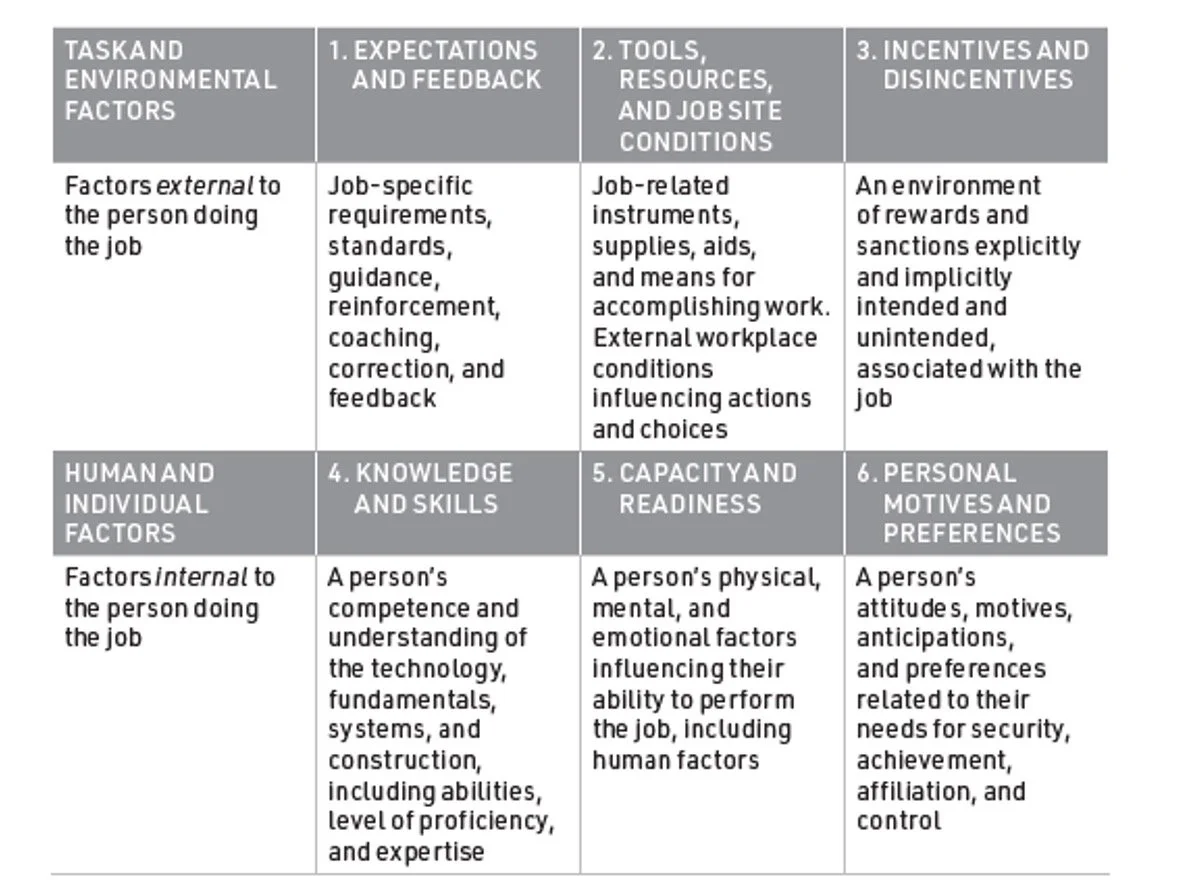
There are multiple adaptations of the original Behavior Engineering Model developed by Gilbert. We present an adaptation developed by Tony Muschara. Additional references include Training Ain’t Performance by Harold D. Stolovich and Carl Binder’s Six Boxes.